
screws
A screw is a metal fastener which have helically shaped, tapering, threaded shanks with slotted heads, designed to be driven into wood or other material with a manual or power driver. The threaded shank aspect of screws makes them generally stronger than nails, and are also easier removable while increasing the chances to be able to remove the attached material without too much damage. The gripping strength is based on how much thread is there per inch of shaft. Screws are commonly sized in shank diameter by the gauge (#3, #4, #5, #6, etc…) but they may be sized in other systems as well. There are 7 characteristics of screws which determine their use and classification: Head Type, Material, Length, thread type, points, drive styles, and Diameter. Holes for screws should be pre-drilled or ‘piloted’ and the hole should be equal to or slightly less than the actual diameter of the screw shaft, essentially large enough to prevent splitting but small enough to achieve a good hold. A pilot hole should penetrate the base wood at least 1/2 the length of the planned base material penetration.




‘Countersinking’ is the act of grooving out a hole so the screw head can be flush or recessed with the attached material.
A ‘Self-Tapping’ screw is meant to easily penetrate the material it’s entering and create it’s own female threads as it’s driven

Material Types – Steel (Iron and Carbon) – Or Carbon Steel; Most commonly used screw material type. Strongest but least corrosion resistant.

Brass (2/3 Copper – 1/3 Zinc) Gold in color and used for aesthetic or low friction applications; corrosion resisent, non-magnetic electro-plated finish, common in locks, doorknobs, plumbing, electrical, etc.
Stainless Steel (Iron and Chromium (min 10%)) very high corrosion resistance, 304 and 316 grades most common with over a hundred other grades. Aluminum and Bronze screws also available,

Standard Lengths – 1/2″ – 6″ Drive Styles


Torx (external),
Torx (internal),
Square Socket (Robertson), Hexagon,
Quadrex,
Phillips,
Phillips/Slot Combo,
Slotted,
Phillips/Hex Combo.
Diameter – up to 24 Gauge (#8, #9, etc)
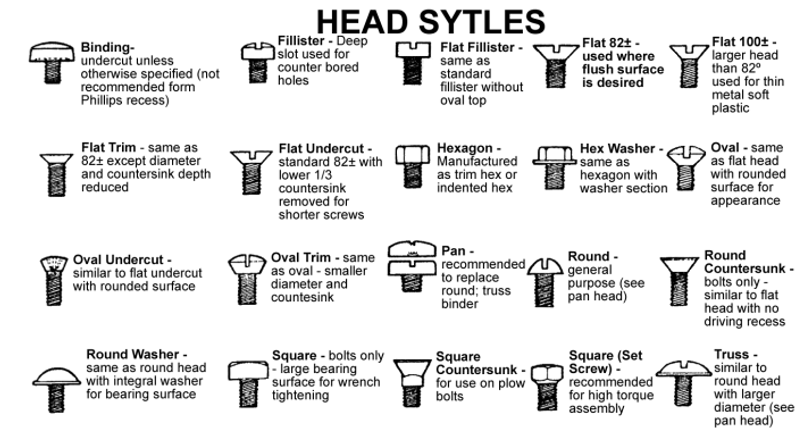
Heads –
(Driver Type) Slotted,
Phillips,
Allen,
Square (Profile) Flat Head,
Oval Head,
Round Head,
Truss Head,
Pan Head,
Fillister Head,
Bugle Head,
Security Head,
Trim,
Cap,
Hex Washer,

Threads – Course, Twin, Fine, Box, Hi-Lo


Points – Sharp Point, Type 17 Point, Drill Point, Pilot Point, Drill Point w/Wings
Wood Screw – Steel most common, with brass 2nd most common, and stainless steel 3rd most common. Should be 1/8″ less than the boards being combined, with at least half of the screws length penetrating the base material. Course-threaded screws are typically for softwoods and fine-threaded for hardwoods.

Drywall Screw – Commonly black, 6 gauge (also come in 7, 8, and 10 gauge), bugle head, with the most common length ranges from 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-5/8″, 2″, 2-1/2″, and 3″. When working with 1/2″ drywall use 1-1/4″ or 1-3/8″ screw lengths. Use coarse drywall screws for attachment to wood and fine threaded drywall screws for attachment to 20-25 gauge light gauge metal studs. High-and Low thread drywall screws are used to attach drywall to light gauge metal studs.

Machine Screw – Have a uniform diameter (no taper or pointed tip) and are most commonly used to fasten machine components, appliances, etc.
Machine Screw – Have a uniform diameter (no taper or pointed tip) and are most commonly used to fasten machine components, appliances, etc.


Cap Screw – Typically made of low carbon steel and are very commonly used in construction or repair projects.
Set Screw – A cscrew used to join two objects together, often without the use of a nut.


Pan-Head Framing Screws – For use attaching light gauge metal studs to light gauge metal tracks (20-25), feature a shorter shank and thicker head. Commonly 7 gauge and 7/16″ long.
Cement Board Screws – Common spade point with nibs, meant to fasten cement board to wood or light gauge metal framing. Nibs under head allow countersink, spade point penetrates board without cracking, high-low threads provide strength, chemical coating resists corrosion.

